Crack Width Calculation Euro Code 2 Slab With Opening
- Crack Width Calculation Eurocode 2 Slab With Opening Dates
- Crack Width Calculation Eurocode 2 Slab With Opening Date
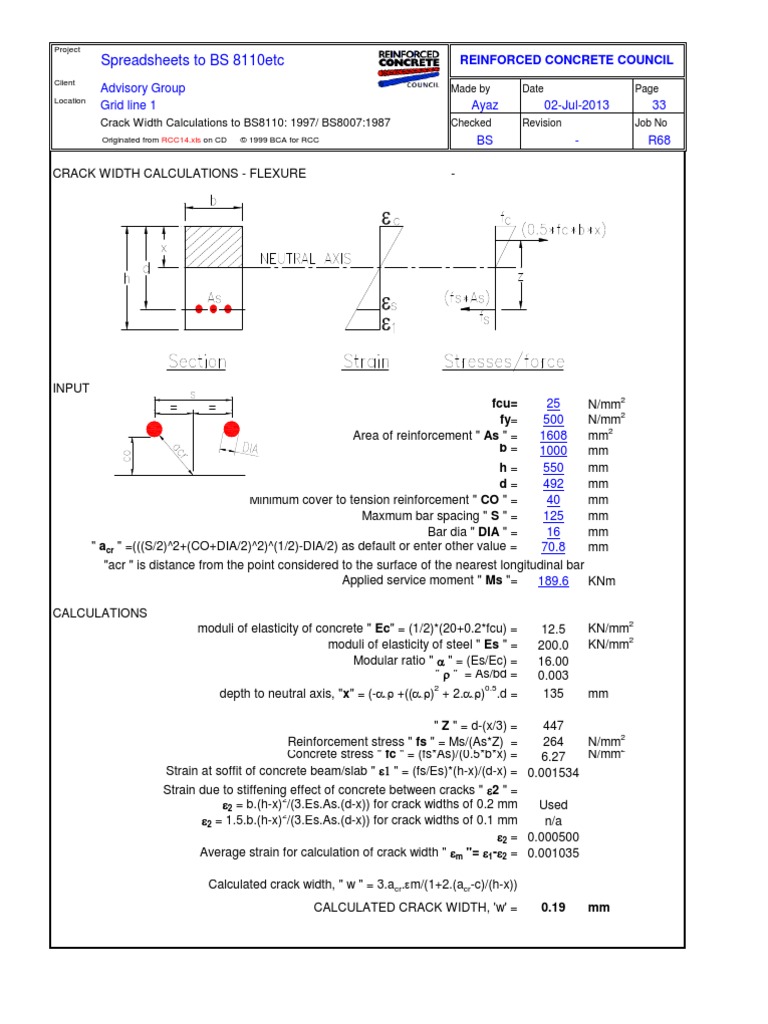
Last Updated on Sun, 17 Jul 2011 When cracking occurs as a result of restraint to shrinkage or thermal effects then the bar sizes must be limited as indicated in table 6.9. But the maximum spacing limits of table 6.7 do not need to be applied. The steel stress to be used in table 6.9 can be calculated from equation 6.3 where /ls.prm. Is the steel area provided at the section under consideration and As.mi„ is given in equation 6.2.6.1.8 Side face and surface reinforcement in beamsIn beams over 1 m deep additional reinforcement must be provided in the side faces to control cracking as indicated in figure 6.2(a). This reinforcement should be distributed evenly between the main tension steel and the neutral axis and within the stirrups. The (a) (b)minimum area of (his reinforcement can be calculated from equation 6.2 with k taken as 0.5.
In assessing the maximum spacing and size of this reinforcement from (ables 6.7 and 6.9 a stress value equal to one-half of that calculated for the main tensile reinforcement may be used and it may be assumed that (he side face reinforcemem is in pure tension.In addition to the above requirement, EC2 requires that surface reinforcement is provided where it is necessary to control spalling of (lie concrete due to tire (axis distance 70 mm) or where bundled bars or bars greater than 40 mm diameter are used as main reinforcement. In the UK, however, this is not adopted due to practical difficulties in providing such reinforcement. For high covers it is recommended that additional fire protection is provided and crack width calculations are recommended with large diameter bars.The surface reinforcement, if provided, should consist of welded mesh or small diameter high bond bars located outside the links as indicated in ligure 6.2(b). Cover to this reinforcement must comply with the requirements of section 6.1.1 and the minimum area of longitudinal surface reinforcement should be I per cent of (he area of the concrete outside the links and in the tension zone below the neutral axis: shown as the shaded area in figure 6.2(b). The surface reinforcement bars should be spaced no further than 150 mm apart and if properly anchored can he taken into account as longitudinal bending and shear reinforcement.
6.2 Span-effective depth ratiosThe appearance and function of a reinforced concrete beam or slab may be impaired if the deflection under serviceability loading is excessive. Deflections can be calculated as indicated in section 6.3 but it is more usual to control deflections by placing a limit on the ratio of the span to (he effective depth of the beam or slab. EC2 specifies equations to calculate basic span-effective depth ratios, to control deflections to a maximum of span/250. Some typical values are given in table 6.10 for rectangular sections of class C30/35 concrete and for grade 500 steel. The ratios can also be used for flanged sections except where the ratio of the width of flange to the width of web exceeds 3 when the basic values should be multiplied by 0.8. For two-way spanning slabs, the check for the basic span-effective depth ratio should be based on the shorter span whereas for flat slabs calculations should be based on the longer span.The two columns given in table 6.10 correspond to levels of concrete stress under serviceability conditions: highly stressed when the steel ra(io p exceeds 1.5 per cent and Table 6.10 Basic span-effective depth ratios (fyk - 500N/mm2, C30/35 concrete).
I'm trying to understand how RSA calculates the cracking width in slabs according to Eurocode and I have a few doubts.1 - Is it important that the SLS combinations are 'SLS:QPR' type or any combination can be used?2 - Does RSA ignores the tension resistance of the concrete, ie, for low tension in concrete is it possible to get a crack width of zero?3 - How difference is the RSA analysis when using the 'analytical method' or the 'Wood+Armer method'?4 - One of the info needed for calculation is the diameter of the bars. RSA considers the diameter defined in the 'Reinforcement' tab of the 'Reinforcements Parameters'of each panel?Thanks in advance. Hi Luis,1 - Is it important that the SLS combinations are 'SLS:QPR' type or any combination can be used?Yes, it is2 - Does RSA ignores the tension resistance of the concrete, ie, for low tension in concrete is it possible to get a crack width of zero?RSA considers tension resitance of concrete till tghe moment cracks appear.
Crack Width Calculation Eurocode 2 Slab With Opening Dates

If you are below this stress level the cracks can be displayed as 0s.3 - How difference is the RSA analysis when using the 'analytical method' or the 'Wood+Armer method'?The descriptions of both methods are available in Help. I'd say that the prior is more for walls or when you have large Nxy forces.4 - One of the info needed for calculation is the diameter of the bars. RSA considers the diameter defined in the 'Reinforcement' tab of the 'Reinforcements Parameters'of each panel?Correct.If you find your post answered press the Accept as Solution button please. This will help other users to find solutions much faster.
Hi ArturI have some additional points to clarify.I'm assuming that RSA is calculating the cracking width according to clause 7.3.4 of Eurocode EN 1992-1-1:2004.1 - Above is expression 7.9 and 7.11 from clause 7.3.4. Is it possible to know the values of the coefficients that RSA considers in calculation? I thinking in the values of fct,eff, alfae, kt, k1, etc.2 - RSA must calculate the stress in the tension reinforcement assuming a cracked section. Is it possible to see those calculated values in each point of a panel? Something like a map of stress in the tension reinforcement?3 - In a model where the panels have some reduction factors applied to their stiffness, when calculating the reinforcements RSA shows a warning like 'Slab is orthotropic.

Calculation is performed for equivalent uniform slab thickness'. How can I know the thickness that is been considered?Thanks in advance. Hi Luis,wrote:Hi ArturI have some additional points to clarify.I'm assuming that RSA is calculating the cracking width according to clause 7.3.4 of Eurocode EN 1992-1-1:2004.1 - Above is expression 7.9 and 7.11 from clause 7.3.4.
Crack Width Calculation Eurocode 2 Slab With Opening Date
Is it possible to know the values of the coefficients that RSA considers in calculation? I thinking in the values of fct,eff, alfae, kt, k1, etc.No, as there is no calculation note for the theoretical reinforcement for panels they are not displayed.2 - RSA must calculate the stress in the tension reinforcement assuming a cracked section. Is it possible to see those calculated values in each point of a panel? Something like a map of stress in the tension reinforcement?No, such kind of maps is not available.3 - In a model where the panels have some reduction factors applied to their stiffness, when calculating the reinforcements RSA shows a warning like 'Slab is orthotropic. Calculation is performed for equivalent uniform slab thickness'.
How can I know the thickness that is been considered?The one from the Th field.If you find your post answered press the Accept as Solution button please. This will help other users to find solutions much faster.





